Millions worldwide wrestle with diabetes, a prevalent and complex health condition that necessitates comprehensive understanding. The disease presents itself in two primary forms which are Type 1 and Type 2. This article explores the nuances of diabetes symptoms, and investigates effective treatments for both types, offering essential insights into managing this condition optimally.
Differentiating Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Distinguishing between Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, an autoimmune condition and a metabolic disorder respectively, is paramount to comprehending the nuances of diabetes symptoms. In particular, understanding how Type 1 unfolds when insulin-producing cells fall victim to a mistaken attack by the body's immune system. This depletion renders survival impossible without external insulin. Hence, it is necessary for sustained life through injections. Contrarily, insulin resistance, a condition in which the body's cells fail to respond efficiently to insulin primarily instigates Type 2 diabetes. Lifestyle factors such as diet and physical activity contribute to the development of this disease. Healthcare professionals must recognize these distinctions. They must tailor suitable treatment plans for patients, guaranteeing precise diagnosis and efficient management.
These differences highlight the critical need for personalized care and targeted interventions specific to each type of diabetes. This enhances not just effectiveness but also efficiency in treatment strategies overall.
- Genetic Factors in Type 1 and Type 2: While genetics play a predominant role in Type 1 diabetes, Type 2 diabetes involves a more intricate interplay between genetics and lifestyle factors.
- Age of Onset: Type 1 diabetes is commonly diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, whereas Type 2 diabetes is typically identified in adulthood, highlighting the need for age-specific diagnostic and management approaches.
Unraveling the Symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes
Distinctive symptoms of Type 1 diabetes often emerge rapidly, demanding prompt attention such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, and extreme fatigue. Hallmark indicators include not only these but also potential blood sugar fluctuations signaled by abrupt mood swings and irritability in individuals. Prompt recognition of these signs is imperative. It allows for early diagnosis. Furthermore, it initiates effective management strategies.
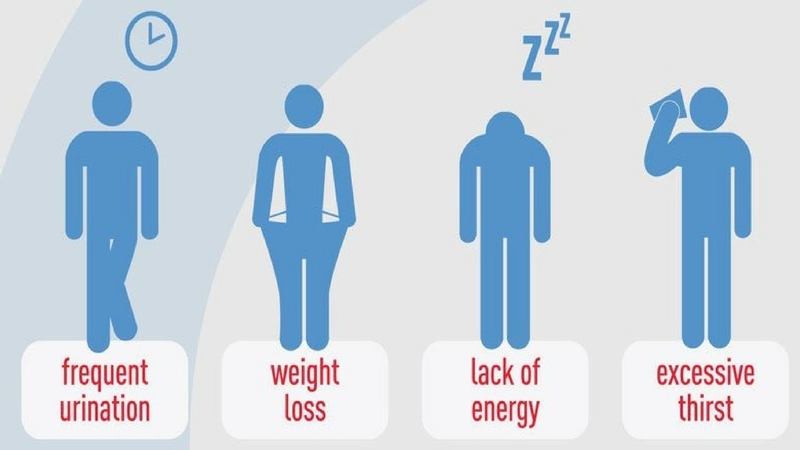
Exploring the intricacies of Type 1 diabetes symptoms further, we must grasp its psychological impact. Managing a chronic condition not only imposes an emotional toll but also, when combined with physical manifestations, can escalate stress and anxiety. This emphasizes the necessity for holistic healthcare approaches. These strategies should tackle not just the physiological symptoms but also the mental and emotional health of individuals with Type 1 diabetes.
- Psychological Impact: Beyond physical symptoms, Type 1 diabetes can have a significant psychological impact, necessitating comprehensive care that addresses mental and emotional well-being.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regular and vigilant blood sugar monitoring is a cornerstone in the management of Type 1 diabetes, providing crucial insights for timely adjustments in treatment plans.
Deciphering the Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
The symptoms of Type 2 diabetes typically manifest in a subtle, gradual manner that can easily be overlooked are increased thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, and slow-healing wounds are among the most common indicators. Persistent fatigue and unrelenting hunger also act as potent markers for this condition. Individuals must be aware of these subtler symptoms to promptly seek medical attention. This facilitates timely intervention, potentially leading to improved long-term outcomes.
To truly understand Type 2 diabetes symptoms, we must recognize the intricate connection between this condition and cardiovascular health. Those afflicted with Type 2 diabetes face escalated risks of heart-related complications. Thus, underlining our imperative to adopt a comprehensive management approach that incorporates routine cardiovascular evaluations and interventions.
- Cardiovascular Risk: Type 2 diabetes is associated with an elevated risk of cardiovascular complications, highlighting the importance of comprehensive management that addresses both diabetes and cardiovascular health.
- Regular Eye Examinations: Routine eye examinations are crucial for individuals with Type 2 diabetes, aiding in the early detection of potential complications such as diabetic retinopathy.
Navigating Treatment Strategies for Type 1 Diabetes
A multifaceted approach to Type 1 diabetes management effectively hinges on daily insulin injections. These serve as a cornerstone. Advanced technologies, such as insulin pumps, provide an even more flexible and precise method of delivering insulin. Essential components of an integrated treatment plan for Type 1 diabetes include adopting a well-balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and closely monitoring blood sugar levels.
Continuous glucose monitoring systems, delving into the technological advancements in Type 1 diabetes management. These pivotal tools offer real-time insights into blood sugar levels. They enable individuals and healthcare professionals to make informed decisions. They facilitate adjustments to insulin therapy, a critical component of effective diabetes care. When such cutting-edge technologies are incorporated, precision and individualization surge within Type 1 diabetes treatment.
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems: Technological advancements, such as continuous glucose monitoring systems, offer real-time insights, enabling more precise and individualized management of Type 1 diabetes.
- Importance of Community Support: Building a supportive community is integral to managing Type 1 diabetes, fostering shared experiences and insights that contribute to improved emotional well-being.
Strategies for Treating Type 2 Diabetes - A Holistic Approach

Beyond medications, the management of Type 2 diabetes integrates lifestyle modifications for comprehensive care including a healthy diet, regular physical activity, and weight management. The foundational pillars consist of these three elements. When prescription medications come into play, they aim to regulate blood sugar levels. Enhancing insulin sensitivity and fostering long-term control over Type 2 diabetes. These are the instrumental results that lifestyle changes prove.
In the exploration of crucial lifestyle modifications for managing Type 2 diabetes, dietary considerations hold a central position such as adopting a low-glycemic diet and abundant in fiber and nutrients. This choice can significantly enhance blood sugar control. Furthermore, when this approach to nutrition intertwines with routine exercise. It forms an exceptionally potent strategy in the holistic management of Type 2 diabetes.
- Low-Glycemic Diet: Embracing a low-glycemic diet, rich in fiber and nutrients, is an effective strategy for managing Type 2 diabetes and promoting better blood sugar control.
- Individualized Exercise Plans: Tailoring exercise plans to individual preferences and capabilities enhances adherence, contributing to the overall success of Type 2 diabetes management.
Conclusion
Understanding the unique symptoms and treatment approaches for Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes is crucial for individuals, caregivers, as well as healthcare professionals. Adeptly navigating these nuances empowers proactive management. Consequently, fostering an improved quality of life among those grappling with this widespread health condition.