The heart is an important organ that sends blood all over the body so tissues and organs can get oxygen and nutrients. Reduced cardiac output (DCO) happens when the heart can't pump enough blood to meet the body's metabolic needs. This means that organs and muscles don't get enough oxygen and nutrients. This can be caused by heart failure, myocardial infarction (heart attack), cardiac arrhythmias, and valvular heart disease, among other health problems. DCO can cause many symptoms that vary in how bad they are and how long they last. Depending on what's causing the cardiac dysfunction and how bad it is, these symptoms may occur slowly or all at once.
Some of the most common signs of DCO are tiredness, weakness, shortness of breath, dizziness or fainting, chest pain, swelling, a fast heartbeat, less urine output, confusion or trouble thinking, pale or cool skin, and stomach problems. If you have any of these symptoms, you should see a doctor immediately because DCO can be a sign of a serious health problem that must be treated immediately. A thorough medical evaluation, including a physical exam and diagnostic tests, can help determine what's causing DCO and suggest the best way to treat it.
Reduced cardiac output, or DCO, is a condition in which the heart can't pump enough blood to meet the body's metabolic needs. This can cause a wide range of symptoms and be a sign of several underlying health problems, such as heart failure, myocardial infarction (heart attack), and cardiac arrhythmias. Here is a full list of the signs and symptoms of a lower cardiac output:
Weariness and A Lack Of Strength
People often feel tired and weak when the heart's output is low. The muscles and organs get less oxygen and nutrients when the heart doesn't pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. This makes the muscles and organs tired and weak.
Feeling Out Of Breath
Another common sign of low cardiac output is shortness of breath. When the heart can't send enough blood to the lungs, the lungs might not get enough oxygen, making breathing hard. This could get worse when you move around or lie down.
Vertigo and Fainting
When the heart doesn't pump enough blood and oxygen to the brain, this can cause dizziness or fainting. This can happen suddenly and without warning, especially when getting up from sitting or lying down after being still.
Pain In The Chest
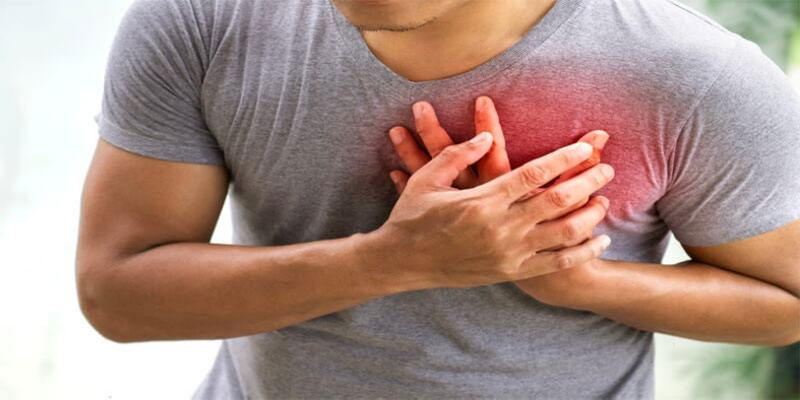

When you work out or are stressed, your heart may not pump as well, which can cause chest pain. This could be a sign of angina, a condition in which the heart muscle doesn't get enough blood and oxygen.
Swelling
Because the heart isn't pumping well, the feet, ankles, or legs may swell. This happens because the heart can't send enough blood to the kidneys, which causes fluid to build up in the body.
Rapid Heartbeat
Due to decreased cardiac output, the heart may beat quickly or oddly. This could be a sign of arrhythmia, which happens when the heart's electrical system isn't working right.
Decreased Urine Output
You may make less urine if your heart isn't pumping as well. This is because the kidneys don't get enough oxygen and blood, which makes them make less urine.
Confusion Or Impaired Thinking
Low cardiac output can confuse or make it hard to think. This is because the brain doesn't get enough blood and oxygen, which makes it hard to think clearly.
Pale or Cool Skin
Because the heart isn't pumping as well, the skin may look pale or feel cool. This is because the heart can't pump enough blood to the skin, which decreases blood flow and cools the skin.
Gastrointestinal Symptoms

Because the heart isn't pumping as well, you might feel sick, throw up, or have pain in your stomach. This is because the digestive system isn't getting enough blood and oxygen, which causes problems with digestion.
Conclusion
Decreased cardiac output is a condition that can cause several different symptoms, such as tiredness, shortness of breath, chest pain, dizziness, and problems with the digestive system. When the heart can't pump enough blood to meet the body's metabolic needs, oxygen and nutrients can't reach the organs and muscles. This causes these symptoms. If you have any of these symptoms, you should see a doctor immediately because DCO can be a sign of a serious health problem that must be treated immediately. A thorough medical evaluation, including a physical exam and diagnostic tests, can help determine what's causing DCO and suggest the best way to treat it. DCO can be managed, and the health of the person as a whole can get better with the right diagnosis and treatment.