In the world of fitness, trends come and go, but not all are as safe as they seem. One such trend, dry scooping, has taken social media by storm, with influencers swearing by it as a way to boost their energy before hitting the gym. The idea is simple: swallow a scoop of pre-workout powder without water, expecting instant results. But heres the catchwhat looks like a harmless shortcut could actually be dangerous.
Behind the quick-fix promise lies a list of serious health concerns that many might not consider before trying it themselves. Let's explore why health experts strongly urge people to think twice before embracing this risky pre-workout practice.
What Is Dry Scooping?
At its core, dry scooping is the act of ingesting a pre-workout supplement in powder form without first mixing it with water. Traditionally, pre-workout powders are designed to be dissolved in water and consumed as a drink 20-30 minutes before exercise. These supplements often contain ingredients like caffeine, creatine, and amino acids, which aim to boost energy levels, improve endurance, and increase focus during workouts.
The appeal of dry scooping comes from the belief that consuming the powder in this undiluted form allows for quicker absorption, potentially leading to faster and more pronounced effects. Fitness influencers and social media trends have played a significant role in popularizing this practice, making it appear like an efficient and effective method for getting an extra boost. However, health professionals warn that the reality is far less appealing.
The Health Risks of Dry Scooping
While dry scooping may look like a shortcut to enhanced performance, it poses several health risks that should not be ignored. Experts warn that bypassing the recommended preparation process of pre-workout powders can have serious consequences for the body.
Risk of Choking and Aspiration
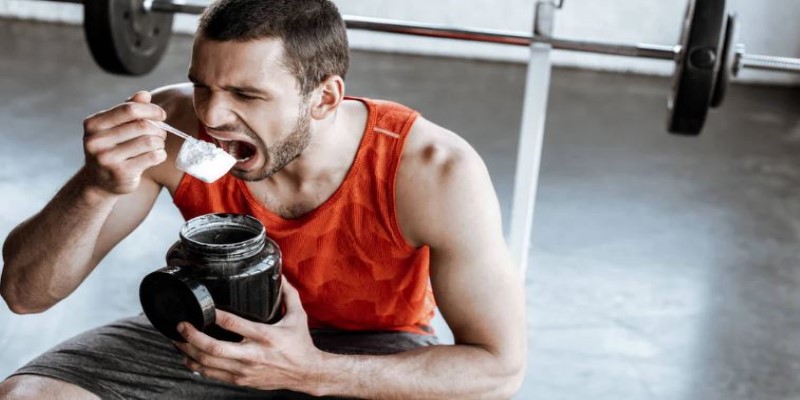

Pre-workout powders are not intended to be consumed dry, and doing so increases the risk of choking. Without water, the powder can become lodged in the throat, making it difficult to breathe. In some cases, the powder may be accidentally inhaled, leading to aspiration, where substances enter the lungs. This can result in coughing, wheezing, or even more severe respiratory complications, especially for those with underlying health conditions.
Overloading the Body with Stimulants
Many pre-workout supplements contain high doses of caffeine and other stimulants. Symptoms of caffeine overdose include rapid heartbeat, dizziness, nausea, and anxiety. In extreme cases, excessive caffeine intake can trigger heart palpitations, high blood pressure, or even cardiac events, particularly in individuals with pre-existing heart conditions.
Gastrointestinal Issues
Dry scooping can also cause significant digestive discomfort. Pre-workout powders contain a variety of ingredients designed to be diluted with water for easier digestion. Consuming them dry can lead to stomach cramps, nausea, and diarrhea. Additionally, without water, the body may struggle to break down and absorb the ingredients, leading to reduced effectiveness and potential digestive irritation.
Dehydration
Pre-workout supplements are meant to be taken with water for a reason. Not only does water aid in the digestion and absorption of the powders ingredients, but it also helps maintain hydration levels. Exercise already places stress on the body, and adding the dehydrating effects of a concentrated dose of caffeine and other stimulants can lead to dehydration. This can be especially dangerous during intense physical activity, where hydration is critical for performance and safety.
Why Water Matters in Pre-Workout Supplements?
The design of pre-workout supplements takes into account the need for proper hydration. When mixed with water, the powder dissolves, ensuring that the active ingredients are delivered to the body gradually. This allows for better absorption and minimizes the risk of overwhelming the system.
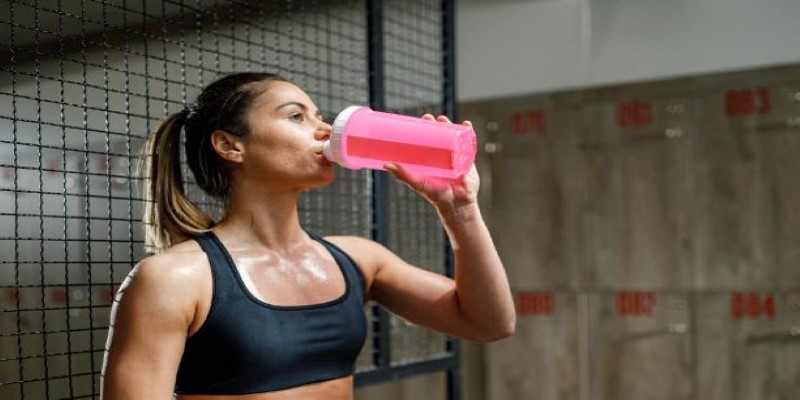

Water also plays a crucial role in diluting the stimulants in pre-workout supplements, helping to prevent a sudden spike in heart rate or blood pressure. Moreover, proper hydration supports overall athletic performance, improving endurance and reducing the risk of injury during exercise. By skipping the water, individuals practicing dry scooping are not only exposing themselves to potential health hazards but also potentially reducing the benefits of the supplements they are consuming.
The Role of Social Media in Promoting Dry Scooping
One of the primary drivers behind the dry scooping trend is social media, where influencers and fitness enthusiasts often share their workout routines and supplement habits. Platforms like TikTok and Instagram are filled with videos of people dry scooping, with many claiming it gives them an immediate burst of energy before exercising. These viral trends can make the practice seem exciting and effective, especially to younger individuals who may be less aware of the risks involved.
However, experts caution that social media is not always a reliable source of health advice. Just because a practice is popular online does not mean it is safe or beneficial. In fact, many health professionals have taken to these same platforms to debunk the myths surrounding dry scooping, emphasizing the importance of following the instructions provided by supplement manufacturers.
Conclusion
Dry scooping may seem like a convenient way to enhance workout performance, but the risks far outweigh the potential benefits. From choking hazards to heart complications, the dangers associated with this trend are real and significant. Health experts advise against this practice, urging individuals to stick to safer methods of supplement consumption. Following the proper guidelines, staying hydrated, and focusing on a balanced diet are far more effective ways to support fitness goals without putting your health at risk.
As with any fitness trend, its essential to prioritize safety and listen to expert advice over viral challenges. When it comes to dry scooping, the warnings from health professionals are clear: this is one trend that should be left behind in favor of safer, more effective workout strategies.